
New COVID-19 Variant NB.1.8.1: Symptoms, Spread, and Safety Tips
NB.1.8.1 variant is a newly identified Subline of the Omicron variant of COVID-19, which has recently been associated with an increase in global transmission rates. This version increases broadcast capacity and may be entitled to immune-evidence properties, increasing anxiety among health experts. While its symptoms meet in the previous Omicron strains – such as fever, cough, fatigue, and sore throat – some individuals report a few diverse or acute signs. Most cases remain mild, but the virus may pose a greater threat to weak immunity or persons with pre-existing conditions. As the investigation continues, public health officials recommend staying updated on vaccination, practicing hygiene, and taking preventive measures to limit the spread.
What is the COVID-19 Variant NB.1.8.1?
NB.1.8.1 version is a new emerging subvariant of the Omicron dynasty of the Sars-CoV-2 virus, which causes COVID-19. Like other Omicron subvariants, NB.1.8.1 has evolved through genetic mutations, especially in spike proteins of the virus, which can affect how easily it spreads and how well it develops existing immunity from vaccines or previous infections.
While detailed scientific data is still being assembled, initial indications suggest:
- This may be more transmissible than the first Omicron strains.
- It can have a mild immune ability to avoid, which means that it can partially bypass protection from previous infections or vaccinations.
- Most cases associated with NB.1.8.1 are reported to be mild to moderate, especially among vaccinated persons.
NB.1.8.1 is currently subject to close observation by global health authorities as they monitor its behavior, infection rate, and possible impact on public health. Although it is not yet classified as a type of concern by the World Health Organization (WHO), awareness and preventive action are important to manage its spread.
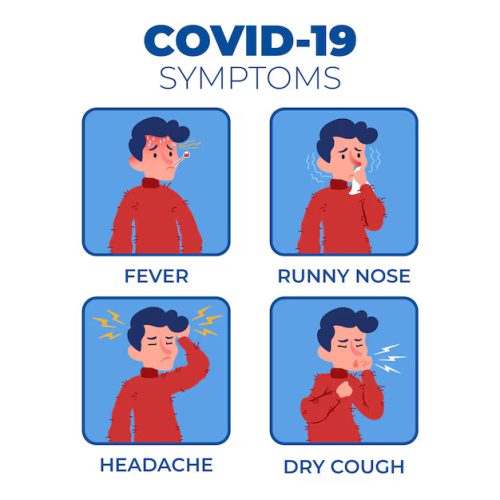
Symptoms of New COVID-19 Variant (NB.1.8.1)
NB.1.8.1 COVID variant presents symptoms that are largely similar to previous Omicron sub-variants, although some individuals report a slight difference in severity and duration. Most cases remain mild to moderate, particularly in individuals who are vaccinated or previously exposed to the virus. However, it is important to closely monitor the symptoms, as this version can still lead to health risks, especially for underlying conditions, older adults, or people with low immunity.
People infected with NB.1.8.1 often develop symptoms such as respiratory and flu symptoms within 2–5 days after exposure. Preliminary identification and testing can help reduce proliferation and ensure timely care.
General Symptoms:
- Feverish
- Constant dry cough
- sore throat
- Stuffed nose
- Headache
- Muscle or body pain
- Fatigue and weakness
Less Common or Additional Symptoms:
- Breathing or difficulty in breathing (mainly in severe cases)
- Loss of taste or odor (now less frequent than the first variant)
- Light gastrointestinal issues such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Chest inconvenience
- Skin rashes in rare cases
Symptoms in children:
- Mild fever
- Irritability
- Throat
- Lower hunger
While many patients recover with comfort and hydration, any symptoms of deteriorating symptoms, especially difficulty breathing or chest pain, should be paid immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and proper separation are important for managing the spread of NB.1.8.1.
Why Is NB.1.8.1 Concerning?
- High Transmissibility
NB.1.8.1 quickly spreads, especially in the indoor environment. Like other Omicron variants, it can be transmitted more efficiently, making it difficult to control without public health measures.
- Immune Evasion
Preliminary research suggests this subvariant may partially evade immunity acquired from previous infections or vaccinations. While vaccines still offer strong protection against severe illness and hospitalization, breakthrough infections are being observed more frequently.
- Strain on Healthcare Systems
An increase in cases can lead to a surge in hospital visits, putting pressure on healthcare resources and staff. Even if many cases are mild, a small percentage requiring hospitalization can escalate quickly in densely populated areas.
Should You Be Worried?
It’s natural to feel concerned during uncertain health situations, such as the emergence of a new virus variant or outbreak. However, being informed and prepared is more effective than worrying. If you are vaccinated, practice good hygiene, monitor symptoms, and follow public health guidance, the risk of serious illness remains low for most healthy individuals. Focus on prevention rather than panic.
When Should You Be More Cautious?
If You Have Chronic Illnesses – Conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or lung problems may increase risk.
If You’re a Senior Citizen – Older adults may have weaker immunity and need extra precautions.
If You’re Immunocompromised – People undergoing treatments like chemotherapy or with autoimmune disorders should stay alert.
If You’re Unvaccinated – Without vaccine protection, risk of complications may be higher.
If You’re Experiencing Symptoms – Seek timely testing and medical advice for early detection and care.
Staying calm, informed, and proactive is the best way to protect yourself and those around you.
How to Spread the New COVID-19 Variant?
COVID‑19 spreads primarily through respiratory routes, and new variants like NB.1.8.1 follow the same patterns. Understanding how it transmits helps you better protect yourself and others.
How the New COVID‑19 Variant Spreads?
New variants spread via the same means as previous strains—they don’t travel through new mechanisms.
- Respiratory droplets & aerosols: Infected individuals expel virus‑laden droplets when they breathe, talk, cough, sneeze, or sing. These particles can be inhaled directly, especially in close contact or poorly ventilated indoor spaces
- Airborne transmission: Tiny aerosolized particles linger in the air, moving across rooms and persisting for hours, particularly indoors with inadequate ventilation.
- Surface (fomite) contact: Transmission via contaminated surfaces is possible but rare—hand washing minimizes this risk.
- Superspreading events: Large, crowded, and enclosed gatherings are high-risk scenarios where the virus spreads rapidly.
- Pre‑symptomatic & early symptomatic contagion: Individuals can be infectious 4–5 days before symptoms appear and up to 10 days afterward, often peaking around symptom onset.
- Animal-to-human transmission: While documented in animals like mink or deer, spread from animals to humans remains very rare.
Precautions for the New COVID-19 Variant
Following proper safety measures is important to reduce the spread of NB 1.8.1 and protect oneself and others.
1. Vaccinate and stay updated
Vaccination is the most effective way to reduce the risk of serious illness and death. Ensure that you have obtained all recommended doses and boosters, especially if you are in a high-risk group.
2. Wear a mask in public places
Wear high-quality masks like N95 or surgical ones in crowded places, especially when keeping a distance isn’t possible.
3. Practice good hygiene
Clean your hands frequently with soap and water or use hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol. Avoid touching your face.
4. Improve indoor ventilation
Ensure that there is enough airflow to reduce the risk of air being broadcast into homes, offices, and public places.
5. Avoid crowded places when possible
Try to maintain physical distance in high-risk environments such as public transport, concerts, or indoor ceremonies such as indoor ceremonies.
6. Monitor the symptoms if necessary and isolated
If you feel unwell or notice the initial symptoms of COVID-19, then test and separate until you are sure that it is safe to interact with others.
7. Stay Informed
Stay updated with updates from official health organizations such as the WHO, the CDC, or your local health authority.

Conclusion
NB.1.8.1 The emergence of the COVID-19 variant at one time reminds us that the virus is still favorable. While most people infected with this stress experience light to moderate symptoms, its high broadcast and potential immune theft require constant vigilance.
By informing them to follow the security guidelines and promote community responsibility, we can limit the impact of this and future variants. Let’s keep our guard up – not with fear, but with informed action and mutual care.