
Causes of Vitiligo & How to Control It | Understand Why It Happens
Vitiligo is a disorder in which white patches of skin develop as a result of melanocyte destruction, leading to loss of pigmentation. It may be small in the beginning, but it increases over time, impairing appearance and self-image, although it is neither life-threatening nor infectious.

Symptoms of Vitiligo
Early identification of symptoms of vitiligo can allow for treatment early enough. They are:
- White or light spots on the skin
- Premature whitening of hair on the scalp, eyebrow, or beard
- Whitening inside the mouth or nose
- Loss of color in the retina

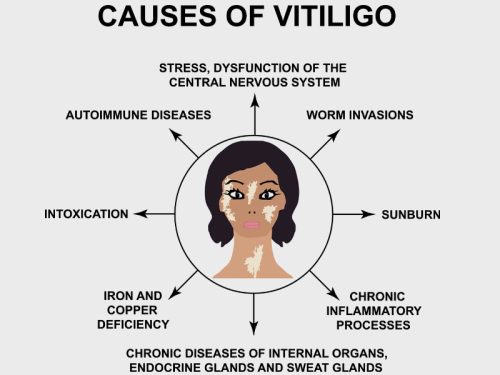
Causes of Vitiligo
Vitiligo occurs when melanocytes, the cells responsible for pigment production, are damaged or cease functioning, leading to white patches on the skin. Its etiology is associated with genetic, autoimmune, and environmental factors.
1. Autoimmune Response
The most widely accepted theory is that vitiligo is an autoimmune disorder, where the immune system wrongly attacks melanocytes, leading to their destruction and loss of skin color.
2. Genetic Predisposition
There is strong evidence that vitiligo is inherited in families. Approximately 20-30% of individuals with vitiligo have a close family member who also has the condition. There are a number of genes involved with immune function that could potentially raise an individual’s chance of developing vitiligo.
3. Neurogenic Factors
Some researchers are of the view that nerve endings in the skin may release chemicals poisonous to melanocytes. This hypothesis is based on the fact that some individuals get vitiligo in areas that have suffered from nerve injury or trauma.
4. Oxidative Stress
Oxidative stress occurs when free radicals exceed the body’s antioxidant defenses, leading to an imbalance and damaging cells. This can cause harm to melanocytes, particularly in individuals with genetic susceptibility. Common triggers include pollution, UV exposure, and an unhealthy diet.
5. Skin Injury or Trauma (Koebner Phenomenon)
Vitiligo patches can occur where the skin has been cut, burned, or injured. This response, referred to as the Koebner phenomenon, indicates that trauma can cause vitiligo in certain people.
6. Endocrine Changes
Endocrine changes—particularly during puberty, pregnancy, or thyroid dysfunction—can affect the functioning of melanocytes. Most individuals with vitiligo also experience thyroid disease, supporting this hypothesis further.
7. Emotional Stress
While stress by itself is unlikely to directly lead to vitiligo, it has been found to exacerbate autoimmune reactions in the body. Individuals who experience prolonged emotional or psychological stress might notice more rapid progression of depigmented areas.
8. Chemical Exposure
Exposure to some industrial chemicals, such as phenols and catechols found in rubber, adhesives, or disinfectants, can destroy melanocytes and cause vitiligo in individuals.
How to Control Vitiligo Naturally?
Vitiligo can be managed naturally in addition to medical therapy. Successful strategies are homeopathy, a healthy diet plan, stress control, herbal remedies, sun management, natural topicals, and lifestyle modifications.
1. Homeopathy Treatment
Homeopathy tries to cure the causes of vitiligo by returning the body to its natural state. Homeopathic remedies are tailored to a person’s signs and symptoms, medical history, and mental state. They tend to improve immunity and aid melanocyte function, which may inhibit white patch advancement and stimulate repigmentation in the long run.
2. Diet and Nutrition
Diet plays a vital role in managing vitiligo. Foods that are antioxidant in nature, such as berries, leafy vegetables, nuts, and seeds, prevent melanocytes from oxidative stress. Foods that are copper-rich, including sesame seeds, cashews, and lentils, contribute to melanin synthesis. Eggs, fish, and green vegetables provide folate and Vitamin B12, which facilitate skin pigmentation. A few people may also find it helpful to exclude triggers such as gluten or dairy.
3. Stress Control
Psychological and emotional stress may worsen autoimmune diseases such as vitiligo. Techniques like meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or writing in a journal can decrease levels of stress. Staying balanced and relaxed emotionally might inhibit the development of further patches of vitiligo.
4. Herbal Remedies
Certain herbs have been used conventionally to assist with skin wellness and melanocyte function:
- Ginkgo Biloba: Being anti-inflammatory, this herb might slow down vitiligo development by enhancing circulation to the skin and activating melanocytes.
- Turmeric: Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory nature means that turmeric can reduce oxidative stress and also assist in skin healing.
- Black Seed Oil: This oil was found to encourage skin regeneration and possibly repigment vitiligo lesions.
5. Sun Exposure
Controlled and moderate sun exposure can stimulate melanin development in the affected spots. But overexposure to the sun should be avoided as it can cause sunburn, making vitiligo worse. Sunscreen should be applied to protect the skin from damaging UV radiation.
6. Topical Treatments
Creams and natural oils may also assist in the maintenance of healthy skin and in inducing repigmentation:
- Aloe Vera: With its healing and soothing nature, aloe vera may reduce irritation and aid in skin regeneration.
- Coconut Oil: Coconut oil contains antioxidants and has the ability to keep the skin hydrated and fix damaged skin.
Papaya Extract: Papaya is rich in enzymes that help stimulate skin cell regeneration and enhance pigmentation.
7. Avoid Chemical Exposure
Harsh chemicals in beauty products, perfumes, or cleaning products may irritate the skin and cause vitiligo. Natural, chemical-free products should be used, and direct contact with toxic substances avoided.
8. Lifestyle Changes
- Stop smoking: Smoking has been associated with the development and worsening of vitiligo, so quitting smoking may be able to manage the condition.
- Drink water: Drinking sufficient water keeps the skin healthy and hydrated.
Homeopathy Treatment for Vitiligo
Homeopathy treatment for vitiligo is aimed at re-establishing immune balance and promoting melanocytes to regain skin color. It is individually tailored to symptoms, mental state, and medical history. By treating such underlying causes as autoimmune disease or hormonal imbalance, homeopathy can be effective in decreasing white patches and, with time, can facilitate repigmentation without the risk of side effects.
Disclaimer
The information given regarding homeopathy treatment of vitiligo is for general information only. Results can differ from person to person, so it is advisable to seek help from a professional homeopathy practitioner before starting any course of treatment. Homeopathic treatment should not be substituted for medical advice or standard treatments.
Consult with Dr. Deepika
Dr. Deepika, the Best Homeopathy Doctor in Noida, has specialized in treating vitiligo with customized homeopathic treatments. With her vast experience, she provides successful, natural remedies to treat the underlying cause and trigger skin repigmentation for long-lasting results.